Experimental Holography
Traditional Setup:
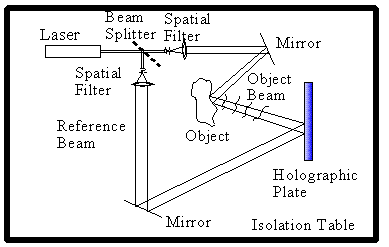 Requirements:
Requirements:
- Monochromaticity : Laser
- Stability : Vibration Isolation Table
- Coherence Length : Keep length of Object Beam and length
of Reference Beam measured from Beam Splitter to
Holographic Plate equal to each other within the
coherence length of the laser (usually a few inches)
- Polarization : Both beams must have same polarization
- Resolution : Special Holographic emulsions (optimized for
wavelength and resolution)
- Beam Strength : Set ratio of Reference to Object beam at
about 6~8 to 1. This places hologram exposure in linear
region of HD curve (light intensity vs film darkening)
for emulsion. If interested in interferometric fringes,
set ratio at about 1~2:1.
- Depth of Field : Keep depth of object within half the
coherence length of laser
Advantages:
- Full-field image
- Non-contact
- Three-dimensional image
Disadvantages:
- Viewable only with laser in dark room (white light
viewable holograms are possible)
- Monochromatic (Multi-Spectral Holograms can be made)
- Speckled appearance (noisy - much of the speckle is
removed if white-light viewable)
- Dark Room Procedures are time-consuming and messy
- Delicate Alignment (some freedom can be obtained by using
Fiber Optics)
Uses:
Industry hasn't shown much interest in straight holography,
and is more interested in holographic interferometry, which gives
quantitative measurement of deflections and deformations. Artists
and advertisers are interested in Display Holography,
but are generally involved with white light holograms. Because of
the information density of a hologram, futurists talk of
holographic data bank elements with huge information storage
capabilities.
Simplification of Holographic Process
- Rigid requirements for setup can be relaxed by using
optical fibers, either monomode or multimode.
- Repositioning difficulties can be eased by developing
film in situ, or by using electronic imaging
techniques.
- Multicolor holograms can be obtained by using lasers with
multiple wavelengths.
- Some types of holograms are viewable in white light -
some reflection holograms, image plane holograms, Benton
(rainbow) holograms.
Reference Texts:
- Collier, R, Burckhardt, C, and Lin, L.: Optical
Holography, Academic Press. A classic work in the
field.
- Unterseher, F., Hansen, J., and Schlesinger, B.: Holography
Handbook, Making Holograms the Easy Way, Ross Books.
A simple practical manual on making holograms.

Send Mail or Comments: matthysd@vms.csd.mu.edu
Last Modified on April 20, 1997
Visitors to this page : 
 Requirements:
Requirements:
 Requirements:
Requirements:
![]()