| Phys 198 | February 2, 1997 |
Problem 4: Polarization. The electric field vector of an incident linearly polarized light wave makes an angle of +30 degrees with the horizontal fast axis of a quarter-wave plate. Describe, in detail, the state of polarization of the emergent wave.
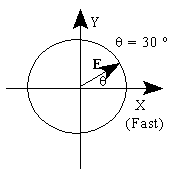
Ex = E cos 30
Ey = E sin 30
Ex > Ey so get elliptical polarization with ellipse' major axis along x axis.
Ex (fast axis) leads Ey (slow axis) by p/2 so first Ex emerges, then Ey;
so CCW or left- handed rotation.
![]()
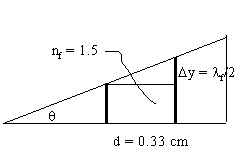
Problem 5: Fizeau Fringes. Fringes are observed when a parallel beam of light of wavelength 500 nm is incident perpendicularly onto a wedge-shaped film with an index of refraction of 1.5. What is the angle of the wedge if the fringe separation is 0.333 cm ?
lf = lo/nf
q = Dy/d
= lo/(2nfd) = 5
x 10-5 rad.
![]()
Problem 6: Grating Orders. Light with a frequency of 4.0 x 1014 Hz is incident on a grating formed with 10,000 lines per centimeter. What is the highest-order spectrum that can be seen with this device? Explain.
a = (1/10,000) cm
l = c/f where c is speed of light
a sin qm = ml
maximum value of sin q = 1
so mmax = a/l = 1.3
need integer value, so mmax = 1
Therefore only the first order can be seen
![]()
Problem 7: Diffraction from a square aperture.
Imagine that you are looking through a piece of square woven
cloth at a point source ( lo
= 600 nm) 20 m away. If you see a square arrangement of bright
spots located about the point source, each separated by an
apparent nearest-neighbor distance of 12 cm, how close together
are the strands of cloth?
d sin qm = ml
set m = 1
q = sin q = y/L
d = Ll/y = 1 x 10-4 m = 0.1 mm
![]()