|
Physics 4, Section
2
Jan 23, 2002
Electric flux Φ is the number of electric
field lines cutting through a surface.
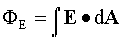
If the surface is closed, Gauss's Law gives a special case for the flux ΦE
through the surface due to the net charge q inside the surface:
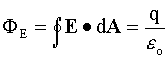 where
where 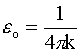
The point of Gauss's Law is that it uses the symmetry of special cases to
simplify the calculation of electric field properties for those cases:
· Point charge : 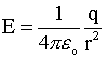
· Line charge : 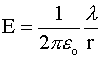
· Sheet of charge: 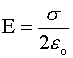
where λ and σ are linear and surface
charge densities, respectively.
Charges on a conductor
For a hollow conductor or a conductor with a cavity, the charge must be on
the outside of the conductor. There is no charge on the inner wall of the
cavity. This is easily shown using Gauss's Law.
Last modified on January 31, 2002
|