Jan 31, 2001
Histogram Specification
Equalization produces a more-or-less uniform histogram. Sometimes it is
desired to modify the input to meet a specified output histogram.
1.
Equalize the input image:
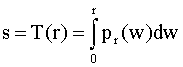
2.
Given the desired output histogram, get the CDF that equalizes the
histogram:
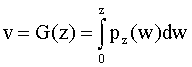
3.
Invert this last equation:
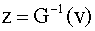
4.
Finally, replace v with s.

Contrast Stretching
Contrast stretching (also known as normalization or autoscaling)
is a method of enhancing image contrast which is more controllable than
histogram equalization. The latter is a fully specified operation with no user
modifications, while the former allows user specification of the input and
output intensity ranges.
Let [a,b] be the lower and upper limits, respectively, of the output
intensity levels, and [c,d] the corresponding limits of the input image. Then
the desired mapping function is
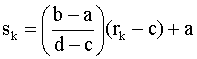

Selective contrast control
