Mar 12, 2001
Image Mapping
In changing the size or orientation of an image, it is frequently necessary
to interpolate pixel values. For example, if it is desired to change an NxN
image to a 2Nx2N image, no one-to-one mapping is possible, and some method of
choosing the values of the inserted pixels must be determined.
·
Replication by nearest neighbor
· Linear interpolation
· Spline interpolation (usually cubic spline)

Linear Image Translation and Rotation
The geometrical result of translating, rotating, and scaling an image can be
handled by linear algebra methods. Restricting the discussion to two dimensions:
Translation:
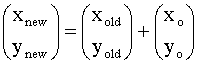 will translate a pixel by (xo, yo)
will translate a pixel by (xo, yo)
Rotation:
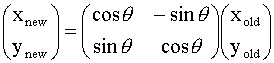 rotates a pixel by q about the origin (0, 0)
rotates a pixel by q about the origin (0, 0)
Scaling:
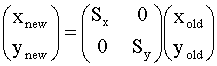 scales an image in x and y directions by Sx and Sy.
scales an image in x and y directions by Sx and Sy.
If negative scaling factors are used, the new image will be flipped about the
axis with the negative scaling factor.

Last modified on February 28, 2001
